The Northwest Territories experienced a lower than average fire season this year, the territorial government says.
According to ENR, the wildland fire season in the Northwest Territories begins May 1st and ends September 30th.
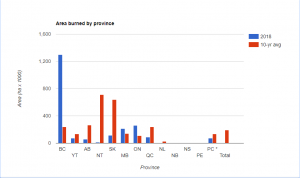
On average, there are 224 wildland fires in the NWT every year, 88 per cent of which are caused by lightning.
As of August 22 this year, there were just 54 fires with a total of 11,271 hectares burnt. The 25-year average is 172 fires and 402,976 hectares burnt.
It’s regular practice for the GNWT to lend resources to more active jurisdictions when the territory experiences a downturn in fire danger.
As partners in the Canadian Inter-agency Forest Fire Centre (CIFFC), ENR personnel and resources were sent to support wildland fire responses in British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Parks Canada, Yukon Territory and Ontario.
Crews that remained in the NWT this season assisted with wildland fire management by performing FireSmart actions and maintenance, such as clearing fire breaks and managing overgrown vegetation, to ensure future protection of communities and other values at risk.
“I am proud of the integrity and hard work shown by our wildland fire personnel this fire season, both at home and while assisting other jurisdictions,” says Robert C. McLeod, Minister of Environment and Natural Resources in a statement.
“Exporting crews not only provides support to our partners in dealing with heavy fire loads, but it also provides valuable experience to northerners who get a chance to work in new environments with crews from across Canada and North America.”
The GNWT sent a total of 76 Type-1 firefighters, 19 overhead staff and 3 air tanker groups to British Columbia and Ontario during this year’s fire season.
Crews and other personnel from all five regions in the territory carried out FireSmart project work, including brush clearing, maintenance on fire breaks and creating temporary helipads.








